蓝牙(Bluetooth)是丹麦国王Harald的绰号。Sun开发者网站的文章(http://developers.sun.com/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/)中有关于蓝牙的各种信息,其中一些可能是为了纪念Harald后人杜撰的,比如:
Harald Christianized the Danes
Harald controlled Denmark and Norway
Harald thinks notebooks and cellular phones should communicate seamlessly
为了说明如何在应用中使用Android的Bluetooth类,将创建一些工具,连接到蓝牙设备,并传输数据。这个示例代码是基于Android SDK的BluetoothChat示例修改的。修改后通用性更强,可以涵盖更多的Bluetooth应用,并更易于在应用中使用。
在对Android的Bluetooth API进行探索的过程中,我们将具体查看如何使用这些API,以及在具体的应用中如何使用这些代码来实现自己的功能,包括Bluetooth开发的诊断工具。
首先,将进一步了解Bluetooth如何工作,以及其在Android中如何实现。
蓝牙协议栈
本节主要讨论关于Bluetooth协议栈的标准和协议(如图18-1所示)。这些协议和标准是Bluetooth的特征:Bluetooth要移动的数据、要同时连接的设备及延迟等。
蓝牙已经成为独立的网络形式,它是个人局域网(personal area network),或称PAN,也称为微微网(piconet)。在设计上,蓝牙最多连接8个设备,每秒钟最多传输3MB数据。连接的设备必须是近距离的,大约在10m内。Bluetooth在非常低的功率下工作,功率是毫瓦级的。这意味着小电池可以持续很长时间:很小的、轻量级的Bluetooth耳机可以持续通话几个小时,这几乎和你的手机耳机的续航时间一样长,而手机耳机的电池要大得多,因为无线通信信号必须能够达到相对而言更远的距离。
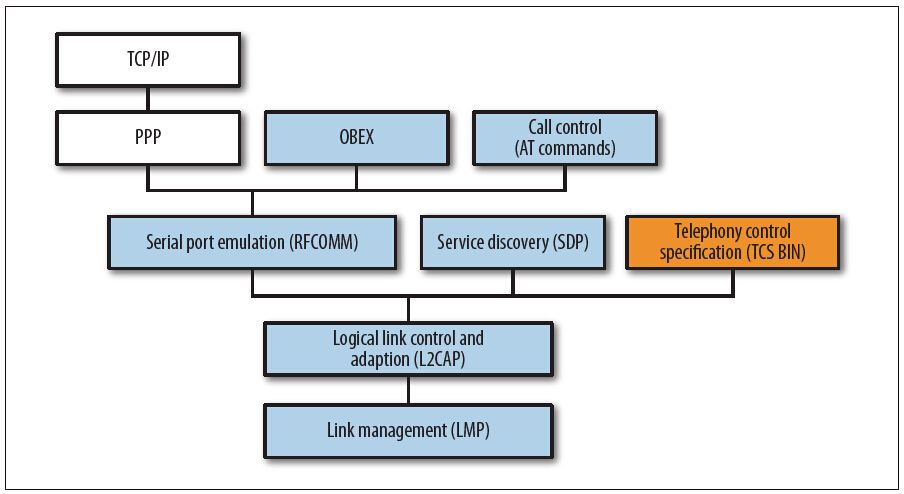
图18-1:Android蓝牙协议栈
可以使用蓝牙的各种设备,包括中低数据传输速率的设备,如键盘、鼠标、平板电脑、打印机、扬声器、耳机以及可能和其他外围设备交流的手机和个人电脑设备等。蓝牙支持PC和手机之间进行连接。
蓝牙特定的协议和adopted协议
考虑蓝牙协议栈的一种有用方法是把蓝牙特定的协议和运行在蓝牙上的adopted协议分离开。总体来说,蓝牙协议和adopted协议可能是极为复杂的,但是如果分别考虑,如运行在蓝牙上的OBEX和TCP/IP大的、复杂的协议,就会更易于理解。因此,我们将从蓝牙较低层的协议开始,集中探讨这些分层在蓝牙的使用中是如何工作的。
另一种有用的设想中的蓝牙模型用于取代串行端口。这意味着蓝牙的较低层可以模拟用于支持你管理外围设备的虚拟串行电缆。这就是我们所使用的蓝牙协议类型。反过来,它又支持我们使用简单的java.io类的InputStream和OutputStream读写数据。
BlueZ:Linux的蓝牙实现
和其他需要连接到电脑和手机的外围设备不同,我们希望手机能连接到所有类型的蓝牙设备。这意味着手机需要相当完整的蓝牙和adopted协议实现,支持建立和管理连接的必要交互,以及通过蓝牙进行通信的应用。
Android使用BlueZ蓝牙协议栈,BlueZ是Linux上最常用的蓝牙协议栈。它取代了名为Open BT的项目。关于BlueZ的信息可以在BlueZ项目网站上获取:http://www.bluez.org。
BlueZ是Qualcomm公司开发的,并被Linux内核采用。BlueZ项目是在2001年开始的,一直是一个活跃的、得到广泛支持的项目。因此,BlueZ是稳定的、可兼容的实现——这也是Linux成为手机操作系统的原因之一。
在Android应用中使用蓝牙
在Android中使用蓝牙意味着使用在其中封装了蓝牙功能的类:Bluez协议栈提供了模拟设备、监听连接及使用连接的方式;java.io包提供了读写数据的类;Handler类和Message类提供了桥接分别负责蓝牙的输入、输出和用户界面的各个管理线程的方式。我们一起来看代码及这些类是如何使用的。
编译和运行这段代码会使你大概了解Android的Bluetooth类可以为需要和附近的设备连接的应用提供了什么功能。
尝试蓝牙应用的第一步是把手机和PC连接起来。然后,需要程序监测PC通过蓝牙接收到了什么,看你在应用中发送的哪些内容被传到了PC上。在这个例子中,我们使用的是Linux工具hcidump。
如果想设置几个断点并执行单步调试,尤其是在应用打开和接受连接那部分,可以在调试模式下启动程序。可以通过PC在Linux或应用中使用Blueman applet创建连接。创建连接之后,在终端执行hcidump命令,查看在PC中接收到的内容。使用下面几个参数控制只显示蓝牙连接的内容:
sudo hcidump -a -R
现在,你在设备中发送内容之后,其会显示在PC上的hcidump输出中。
蓝牙及相关的I/O类
该程序依赖BluetoothAdapter类控制设备的Bluetooth适配器、控制连接设备状态的BluetoothDevice类及负责监听socket并创建连接的BluetoothSocket类。
package com.finchframework.bluetooth;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
public class BtHelperHandler extends Handler {
public enum MessageType {
STATE,
READ,
WRITE,
DEVICE,
NOTIFY;
}
public Message obtainMessage(MessageType message, int count, Object obj) {
return obtainMessage(message.ordinal, count, -1, obj);
}
public MessageType getMessageType(int ordinal) {
return MessageType.values[ordinal];
}
}
BtHelperHandler类定义一些常量,并提供一些封装功能,使得消息相关的方法代码更简洁。
BtSPPHelper.java封装了蓝牙序列号协议(Serial Port Protocol,SPP)的使用:
package com.finchframework.bluetooth;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.UUID;
import com.finchframework.finch.R;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothServerSocket;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
/**
* Helper class that runs AsyncTask objects for communicating with a Bluetooth
* device. This code is derived from the Bluetoothchat example, but modified in
* several ways to increase modularity and generality: The Handler is in a
* separate class to make it easier to drop into other components.
*
* Currently this only does Bluetooth SPP. This can be generalized to other
* services.
*/
public class BtSPPHelper {
// Debugging
private final String TAG = getClass.getSimpleName;
private static final boolean D = true;
public enum State {
NONE,
LISTEN,
CONNECTING,
CONNECTED;
}
// Name for the SDP record when creating server socket
private static final String NAME = "BluetoothTest";
// Unique UUID for this application
private static final UUID SPP_UUID =
UUID.fromString("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
// Member fields
private final BluetoothAdapter mAdapter;
private final BtHelperHandler mHandler;
private AcceptThread mAcceptThread;
private ConnectThread mConnectThread;
private ConnectedThread mConnectedThread;
private State mState;
private Context mContext;
/**
* Constructor. Prepares a new Bluetooth SPP session.
* @param context The UI Activity Context
* @param handler A Handler to send messages back to the UI Activity
*/
public BtSPPHelper(Context context, BtHelperHandler handler) {
mContext = context;
mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter;
mState = State.NONE;
mHandler = handler;
}
/**
* Set the current state of the chat connection
* @param state The current connection state
*/
private synchronized void setState(State state) {
if (D) Log.d(TAG, "setState " + mState + " -> " + state);
mState = state;
// Give the new state to the Handler so the UI Activity can update
mHandler.obtainMessage(BtHelperHandler.MessageType.STATE,
-1, state).sendToTarget;
}
/**
* Return the current connection state.
*/
public synchronized State getState {
return mState;
}
/**
* Start the session. Start AcceptThread to begin a
* session in listening (server) mode.
*
* Typically, call this in onResume
*/
public synchronized void start {
if (D) Log.d(TAG, "start");
// Cancel any thread attempting to make a connection
if (mConnectThread != null) {mConnectThread.cancel; mConnectThread = null;}
// Cancel any thread currently running a connection
if (mConnectedThread != null) {
mConnectedThread.cancel;
mConnectedThread = null;
}
// Start the thread to listen on a BluetoothServerSocket
if (mAcceptThread == null) {
mAcceptThread = new AcceptThread;
mAcceptThread.start;
}
setState(State.LISTEN);
}
/**
* Start the ConnectThread to initiate a connection to a remote device.
* @param device The BluetoothDevice to connect
*/
public synchronized void connect(BluetoothDevice device) {
if (D) Log.d(TAG, "connect to: " + device);
// Cancel any thread attempting to make a connection
if (mState == State.CONNECTING) {
if (mConnectThread != null) {
mConnectThread.cancel;
mConnectThread = null;
}
}
// Cancel any thread currently running a connection
if (mConnectedThread != null) {
mConnectedThread.cancel;
mConnectedThread = null;
}
// Start the thread to connect with the given device
mConnectThread = new ConnectThread(device);
mConnectThread.start;
setState(State.CONNECTING);
}
/**
* Start the ConnectedThread to begin managing a Bluetooth connection
*
* @param socket
* The BluetoothSocket on which the connection was made
* @param device
* The BluetoothDevice that has been connected
*/
private synchronized void connected(BluetoothSocket socket,
BluetoothDevice device) {
if (D)
Log.d(TAG, "connected");
// Cancel the thread that completed the connection
if (mConnectThread != null) {
mConnectThread.cancel;
mConnectThread = null;
}
// Cancel any thread currently running a connection
if (mConnectedThread != null) {
mConnectedThread.cancel;
mConnectedThread = null;
}
// Cancel the accept thread because we only want to connect to one
// device
if (mAcceptThread != null) {
mAcceptThread.cancel;
mAcceptThread = null;
}
// Start the thread to manage the connection and perform transmissions
mConnectedThread = new ConnectedThread(socket);
mConnectedThread.start;
// Send the name of the connected device back to the UI Activity
mHandler.obtainMessage(BtHelperHandler.MessageType.DEVICE, -1,
device.getName).sendToTarget;
setState(State.CONNECTED);
}
/**
* Stop all threads
*/
public synchronized void stop {
if (D) Log.d(TAG, "stop");
if (mConnectThread != null) {
mConnectThread.cancel;
mConnectThread = null;
}
if (mConnectedThread != null) {
mConnectedThread.cancel;
mConnectedThread = null;
}
if (mAcceptThread != null) {
mAcceptThread.cancel;
mAcceptThread = null;
}
setState(State.NONE);
}
/**
* Write to the ConnectedThread in an unsynchronized manner
* @param out The bytes to write
* @see ConnectedThread#write(byte)
*/
public void write(byte out) {
ConnectedThread r;
// Synchronize a copy of the ConnectedThread
synchronized (this) {
if (mState != State.CONNECTED) return;
r = mConnectedThread;
}
// Perform the write unsynchronized
r.write(out);
}
private void sendErrorMessage(int messageId) {
setState(State.LISTEN);
mHandler.obtainMessage(BtHelperHandler.MessageType.NOTIFY, -1,
mContext.getResources.getString(messageId)).sendToTarget;
}
/**
* This thread listens for incoming connections.
*/
private class AcceptThread extends Thread {
// The local server socket
private final BluetoothServerSocket mmServerSocket;
public AcceptThread {
BluetoothServerSocket tmp = null;
// Create a new listening server socket
try {
tmp = mAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord(NAME, SPP_UUID);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "listen failed", e);
}
mmServerSocket = tmp;
}
public void run {
if (D) Log.d(TAG, "BEGIN mAcceptThread" + this);
setName("AcceptThread");
BluetoothSocket socket = null;
// Listen to the server socket if we're not connected
while (mState != BtSPPHelper.State.CONNECTED) {
try {
// This is a blocking call and will only return on a
// successful connection or an exception
socket = mmServerSocket.accept;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "accept failed", e);
break;
}
// If a connection was accepted
if (socket != null) {
synchronized (BtSPPHelper.this) {
switch (mState) {
case LISTEN:
case CONNECTING:
// Situation normal. Start the connected thread.
connected(socket, socket.getRemoteDevice);
break;
case NONE:
case CONNECTED:
// Either not ready or already connected.
// Terminate new socket.
try {
socket.close;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Could not close unwanted socket", e);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
if (D) Log.i(TAG, "END mAcceptThread");
}
public void cancel {
if (D) Log.d(TAG, "cancel " + this);
try {
mmServerSocket.close;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "close of server failed", e);
}
}
}
/**
* This thread runs while attempting to make an outgoing connection
* with a device. It runs straight through; the connection either
* succeeds or fails.
*/
private class ConnectThread extends Thread {
private final BluetoothSocket mmSocket;
private final BluetoothDevice mmDevice;
public ConnectThread(BluetoothDevice device) {
mmDevice = device;
BluetoothSocket tmp = null;
// Get a BluetoothSocket for a connection with the
// given BluetoothDevice
try {
tmp = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(SPP_UUID);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "create failed", e);
}
mmSocket = tmp;
}
public void run {
Log.i(TAG, "BEGIN mConnectThread");
setName("ConnectThread");
// Always cancel discovery because it will slow down a connection
mAdapter.cancelDiscovery;
// Make a connection to the BluetoothSocket
try {
// This is a blocking call and will only return on a
// successful connection or an exception
mmSocket.connect;
} catch (IOException e) {
sendErrorMessage(R.string.bt_unable);
// Close the socket
try {
mmSocket.close;
} catch (IOException e2) {
Log.e(TAG, "unable to close socket during connection failure",
e2);
}
// Start the service over to restart listening mode
BtSPPHelper.this.start;
return;
}
// Reset the ConnectThread because we're done
synchronized (BtSPPHelper.this) {
mConnectThread = null;
}
// Start the connected thread
connected(mmSocket, mmDevice);
}
public void cancel {
try {
mmSocket.close;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "close of connect socket failed", e);
}
}
}
/**
* This thread runs during a connection with a remote device.
* It handles all incoming and outgoing transmissions.
*/
private class ConnectedThread extends Thread {
private final BluetoothSocket mmSocket;
private final InputStream mmInStream;
private final OutputStream mmOutStream;
public ConnectedThread(BluetoothSocket socket) {
Log.d(TAG, "create ConnectedThread");
mmSocket = socket;
InputStream tmpIn = null;
OutputStream tmpOut = null;
// Get the BluetoothSocket input and output streams
try {
tmpIn = socket.getInputStream;
tmpOut = socket.getOutputStream;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "temp sockets not created", e);
}
mmInStream = tmpIn;
mmOutStream = tmpOut;
}
public void run {
Log.i(TAG, "BEGIN mConnectedThread");
byte buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytes;
// Keep listening to the InputStream while connected
while (true) {
try {
// Read from the InputStream
bytes = mmInStream.read(buffer);
// Send the obtained bytes to the UI Activity
mHandler.obtainMessage(BtHelperHandler.MessageType.READ,
bytes, buffer).sendToTarget;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "disconnected", e);
sendErrorMessage(R.string.bt_connection_lost);
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Write to the connected OutStream.
* @param buffer The bytes to write
*/
public void write(byte buffer) {
try {
mmOutStream.write(buffer);
// Share the sent message back to the UI Activity
mHandler.obtainMessage(BtHelperHandler.MessageType.WRITE, -1, buffer)
.sendToTarget;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Exception during write", e);
}
}
public void cancel {
try {
mmSocket.close;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "close of connect socket failed", e);
}
}
}
}
BtSPPHelper类把这些类的使用结合起来,还另外包含了private Thread子类的定义,用于监听、建立连接及维护连接。
这也是java.io包满足Android蓝牙之处:Bluetooth Socket对象包含的方法会返回InputStream对象和Output Stream对象的引用,这些引用可以对socket数据进行读写:
package com.finchframework.bluetooth;
import java.util.Set;
import com.finchframework.finch.R;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.Window;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
/**
* Derived from the BluetoothChat example, an activity that enables
* picking a paired or discovered Bluetooth device
*/
public class DeviceListActivity extends Activity {
// Debugging
private static final String TAG = "DeviceListActivity";
private static final boolean D = true;
// Return Intent extra
public static String EXTRA_DEVICE_ADDRESS = "device_address";
// Member fields
private BluetoothAdapter mBtAdapter;
private ArrayAdapter<String> mPairedDevicesArrayAdapter;
private ArrayAdapter<String> mNewDevicesArrayAdapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Set up the window
setContentView(R.layout.device_list);
// Set result CANCELED in case the user backs out
setResult(Activity.RESULT_CANCELED);
// Initialize the button to perform device discovery
Button scanButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_scan);
scanButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener {
public void onClick(View v) {
doDiscovery;
v.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
});
// Initialize array adapters. One for already paired devices and
// one for newly discovered devices
mPairedDevicesArrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,
R.layout.device_name);
mNewDevicesArrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,
R.layout.device_name);
// Find and set up the ListView for paired devices
ListView pairedListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.paired_devices);
pairedListView.setAdapter(mPairedDevicesArrayAdapter);
pairedListView.setOnItemClickListener(mDeviceClickListener);
// Find and set up the ListView for newly discovered devices
ListView newDevicesListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.new_devices);
newDevicesListView.setAdapter(mNewDevicesArrayAdapter);
newDevicesListView.setOnItemClickListener(mDeviceClickListener);
// Register for broadcasts when a device is discovered
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND);
this.registerReceiver(mReceiver, filter);
// Register for broadcasts when discovery has finished
filter = new IntentFilter(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED);
this.registerReceiver(mReceiver, filter);
// Get the local Bluetooth adapter
mBtAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter;
// Get a set of currently paired devices
Set<BluetoothDevice> pairedDevices = mBtAdapter.getBondedDevices;
// If there are paired devices, add each one to the ArrayAdapter
if (pairedDevices.size > 0) {
findViewById(R.id.title_paired_devices).setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) {
mPairedDevicesArrayAdapter.add(device.getName +
"\n" + device.getAddress);
}
} else {
String noDevices =
getResources.getText(R.string.none_paired).toString;
mPairedDevicesArrayAdapter.add(noDevices);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy {
super.onDestroy;
// Make sure we're not doing discovery anymore
if (mBtAdapter != null) {
mBtAdapter.cancelDiscovery;
}
// Unregister broadcast listeners
this.unregisterReceiver(mReceiver);
}
/**
* Start device discover with the BluetoothAdapter
*/
private void doDiscovery {
if (D) Log.d(TAG, "doDiscovery");
// Indicate scanning in the title
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(true);
setTitle(R.string.scanning);
// Turn on sub-title for new devices
findViewById(R.id.title_new_devices).setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// If we're already discovering, stop it
if (mBtAdapter.isDiscovering) {
mBtAdapter.cancelDiscovery;
}
// Request discover from BluetoothAdapter
mBtAdapter.startDiscovery;
}
// The on-click listener for all devices in the ListViews
private OnItemClickListener mDeviceClickListener = new OnItemClickListener {
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> av, View v, int arg2, long arg3) {
// Cancel discovery because it's costly and we're about to connect
mBtAdapter.cancelDiscovery;
// Get the device MAC address, which is the last 17 chars in the View
String info = ((TextView) v).getText.toString;
String address = info.substring(info.length - 17);
// Create the result Intent and include the MAC address
Intent intent = new Intent;
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DEVICE_ADDRESS, address);
// Set result and finish this Activity
setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, intent);
finish;
}
};
// The BroadcastReceiver that listens for discovered devices and
// changes the title when discovery is finished
private final BroadcastReceiver mReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction;
// When discovery finds a device
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
// Get the BluetoothDevice object from the Intent
BluetoothDevice device =
intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
// If it's already paired, skip it, because it's been listed already
if (device.getBondState != BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED) {
mNewDevicesArrayAdapter.add(
device.getName + "\n" + device.getAddress);
}
// When discovery is finished, change the Activity title
} else if (BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED.equals(action)) {
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(false);
setTitle(R.string.select_device);
if (mNewDevicesArrayAdapter.getCount == 0) {
String noDevices =
getResources.getText(R.string.none_found).toString;
mNewDevicesArrayAdapter.add(noDevices);
}
}
}
};
}
DeviceListActivity类
活动显示一个对话框,该对话框会列出已知的设备,并支持用户扫描请求设备。不同于一些应用使用Thread子类实现异步I/O并通过Handler子类传递结果给UI线程,BluetoothAdapter的startDiscovery方法启动了一个专用的线程并通过广播intent实现数据通信以传递结果。这里,BroadcastReceiver负责处理这些结果。
BtConsoleActivity类
BtConsoleActivity类创建了一个类似聊天工具的activity来和蓝牙设备进行交互。该activity菜单支持连接到设备上,该activity的main视图是发送和接收到的数据的滚动列表。在屏幕的下方,有一个EditText视图,用于输入要发送到另一个SPP连接端的文本。
Handler类用于把单线程的UI和负责在socket上监听、创建连接和执行IO操作的线程结合起来。